
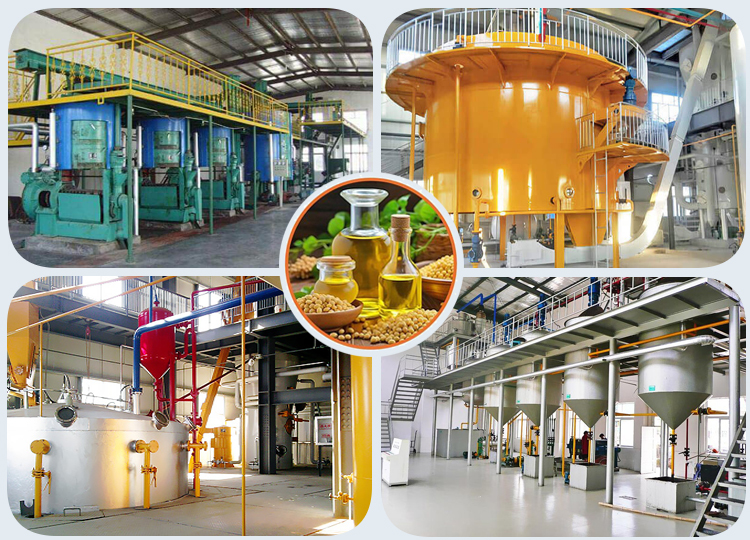
A soybean oil production plant involves several interconnected processes to efficiently extract oil from soybeans and produce high-quality refined soybean oil. The soybean oil production line includes the soybean pretreatment process, soybean pre-pressing process, soybean oil extracting process, and soybean crude oil refining process. With capacities ranging from 100tpd to 5,000tpd, our soybean oil production plants are perfect for meeting the demands of large-scale edible oil production requirements.

Brand
QIE

Raw Material
Soybean

Capacity
100-5000TPD


100-5000TPD
Customized Soybean Oil Production Line On Demand
Highly Intelligent Production In All Sections
Intelligent
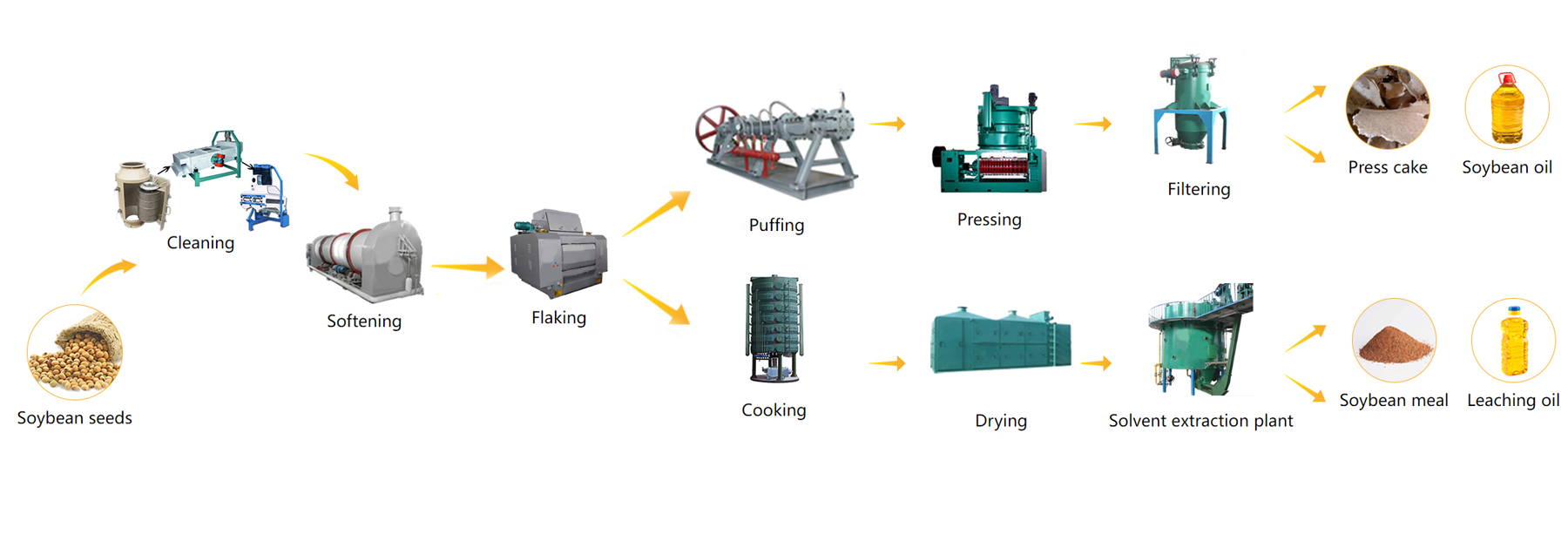

Before entering the workshop to make oil, soybeans need to go through cleaning, crushing, peeling, softening, flaking, cooking, Drying.
In soybean oil production, the choice between mechanical pressing and solvent extraction depends on factors like plant capacity, oil yield requirements, production costs, and intended uses of the by-products (oilcake/meal). The mechanical pressing method is usually a good choice for a soybean oil mill plant with a capacity under 100 TPD. For small to medium production scales, when residual oil in the cake is acceptable or desirable, and when producing high-value, premium, or organic oils, we recommend using the mechanical soybean pressing method. The oil press machines have a capacity ranging from 10 to 300 tons per day (TPD), and they can extract about 70% of the oil in the soybean.
The soybean oil solvent extraction plant is part of the soybean oil processing plant, which is designed to extract oil directly from pressed soybean oil. After the soybean oil solvent extraction plant, the residual oil content in the soybean oil is less than 1%. The pretreated soybean flakes are sent to the soybean solvent extraction plant. The plant uses a type of solvent (normal hexane) to absorb the soybean oil, and then machines separate the solvent from the crude soybean oil. The solvent is used for recycling, and the crude soybean oil is refined in an oil refinery plant.
Pressed cake→Solvent extraction system→D.T.D.C system→Condenser system→Recovery system→Crude soybean oil
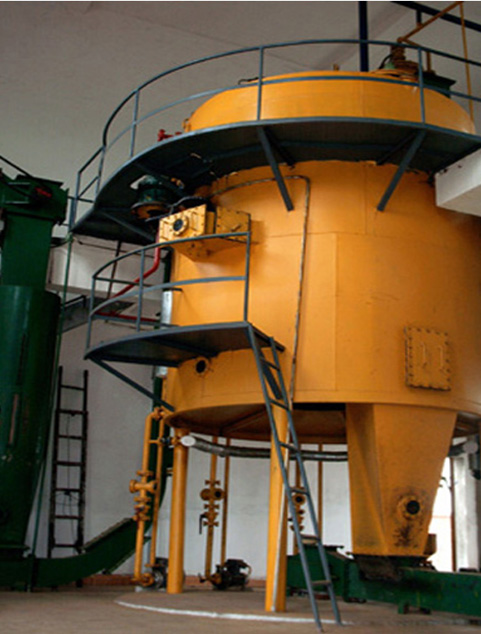

using N-hexane to react with puffing soybean materials, then you can get two parts: the mixture of solvents and oil called miscella oil and the mixture of solvents and meal called wet meal.

D.T.D.C means desolventizer, toaster, dryer and cooler, which is mainly used to separate the solvents from the wet meal, then the dried meal will be sent to meal silo for storage.

since miscella oil contains solvents, we need to separate the solvents from the crude soybean oil by first evaporation, second evaporation and stripping tower, then we can condensate the oil and pump it into a crude oil tank, and you can choose to sell the crude oil to the refinery factory or you can set up a soybean oil refinery plant by yourself.

Usually producing one ton crude soybean oil through the soybean oil solvent extraction method needs around 4kg solvents. Considering of cost-effectives and environmental protection, we add this system to recycle the solvents by condensing it and collecting it for reuse.
We can offer turnkey soybean oil refinery plant solutions from plant layout design, machinery manufacturing, onsite debugging and installing. The production capacity ranges from 5 ton/d up to 1000 ton/day


Degumming Process
Some impurity, such as Phospholipid, gum, and protein, can be dissolved into oil when there is no water, but once there is water in oil, these impurities can be dissolved into water. So, in degumming section of soybean oil refinery plant, we use the hot water to wash crude oil for two-three times to remove these impurities.

Neutralizing/Neutralization Proces
The crude oil is fed into the neutralizer and mixed with small amounts of degumming agent such as phosphoric acid to help remove gums.Free fatty acids are removed from the oil by adding caustic soda and heating it at 60˚ then stirring the mixture. Heating forms soap base, which is then precipitated and collected, and washed with water to remove alkaline particles.

Decolorizing Process
The neutralized oil requires bleaching machine to get rid of colors. This is done by adding the oil in a bleacher machine whereby it is heated to remove any moisture it might have and then mixed with earth bleach and activated carbon. These two properties absorb any colors after which the oil is passed through a filter to separate oil from earth bleach and carbon. The result is golden light oil.

Deodorizing Process
The golden light oil has unpleasant odors which result from materials such as aldehydes, ketones, tocopherols and phenols among other odiferous elements. Deodorizing process of soybean oil refinery plant helps remove these odors by adding the oil in the deodorizer and heating it above at very high temperature and under very high vacuum. This deodorizing process helps get rid of all odors.

QIE Grain and Oil Machinery Co., Ltd
With decades of expertise,QIE Group has successfully installed cooking oil production lines worldwide, serving customers in over 100 countries. Our extensive product portfolio includes cooking oil production solutions, as well as customized solutions for specific capacities ranging from small-scale operations to large conglomerate production facilities.
Whether in Asia, Europe, the Americas or Africa, our equipment is tailored to meet local market needs and production challenges. We operate worldwide and customer satisfaction is at the heart of every project we undertake. From initial consultation and design to installation and after-sales service, QIE Group ensures that every solution meets the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
Get Quote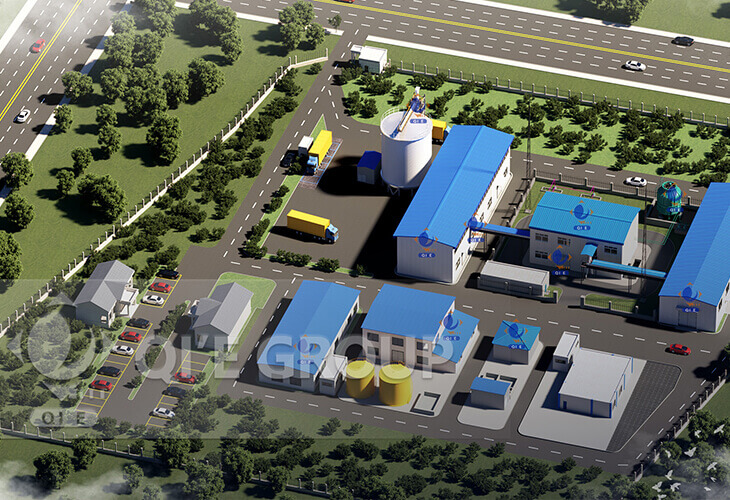

This project includes 300TPD soybean pre-treatment+solvent extraction+30TPD oil refinery plant.
Learn More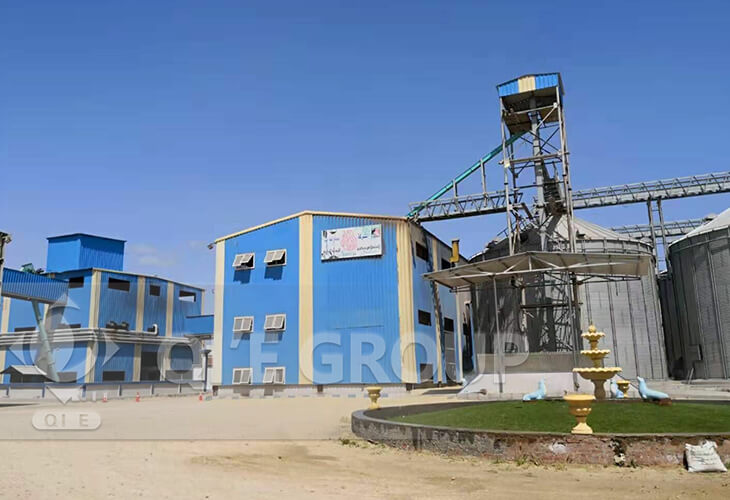

This project includes 300TPD soybean pre-treatment+solvent extraction+60TPD oil refinery plant.
Learn More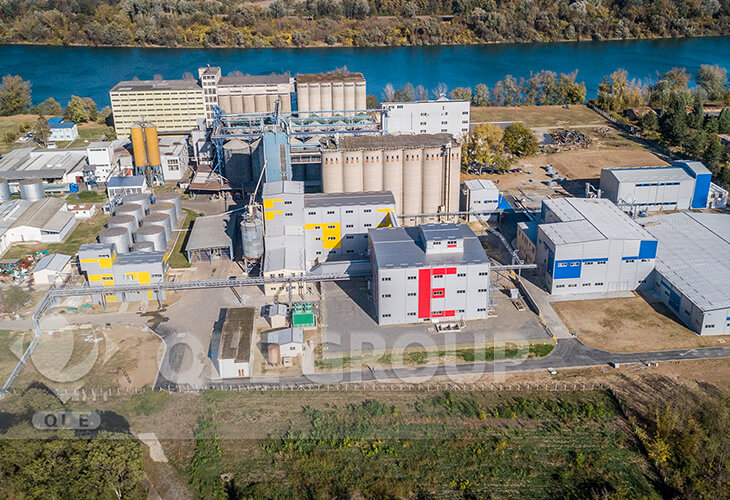

This is our soybean protein isolate project with low temperature desolventing technology in Serbia.
Learn More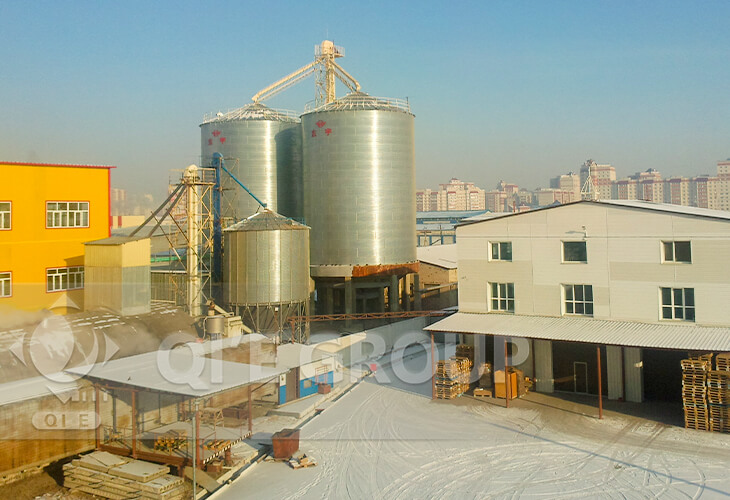

The 200TPD soybean oil project is for our Russian customer.The workshop adopts pretreatment, solvent extraction and refining process.
Learn MoreYes, QIE Machinery offers comprehensive installation and training services to ensure the optimal performance of your equipment. Our services include:
1.Installation Training:
We dispatch experienced engineers to your site to guide the installation, commissioning, and trial operation of your production line. Additionally, we provide thorough training for your operators to ensure stable and safe operations.
2.Technical Support:
Our dedicated service team is available to assist with any technical inquiries, ensuring your equipment operates efficiently.
3.Regular Return Visits:
We conduct periodic follow-ups to assess equipment performance and address any concerns, ensuring long-term satisfaction.
These services are part of our commitment to providing professional and convenient turnkey engineering solutions, from scheme design and equipment production to installation, training, and ongoing technical support.
Cleaning soybean oil mills to prevent residue buildup.
Lubricating moving parts to reduce wear.
Inspecting dies and rollers for signs of damage.
Checking electronic controls for proper calibration.
Soybean oil production lines are categorized by their daily processing capacity, which dictates equipment size, automation, and output:
Cleaning: Removes impurities (stones, metal, dust) via destoners, magnetic separators, and vibratory screens to protect equipment and ensure oil quality.
Conditioning: Adjusts soybean moisture (8–10%) and temperature (60–80°C) to soften seeds, improving oil release during extraction.
Extraction: Either mechanical pressing (screw/expeller presses) or solvent extraction (for higher yield) to separate oil from solids.
Crude oil refining: Removes impurities via degumming (phospholipids), neutralization (free fatty acids), bleaching (pigments), and deodorization (volatile compounds) to produce edible-grade oil.
Oil storage: Stores refined oil in stainless steel tanks with temperature control and nitrogen blanketing to prevent oxidation.
Packaging: Fills oil into bottles, drums, or bulk containers using automated fillers, with labeling for compliance and consumer information.
Energy use varies by scale and extraction method:
Setup time depends on scale and complexity:
Nutritional quality (preserving unsaturated fats, vitamin E, and avoiding trans fats) is maintained through:
Small-scale (mechanical): $5,000–$50,000, depending on capacity and automation.
Medium-scale (semi-automated with basic refining): $50,000–$500,000.
Large-scale (solvent extraction + full refining): $1 million–$10 million+.